RISC
(Risk-Integrated
Software for Clean-ups) is a
unique software package for
evaluating human health risk and determining clean-up levels at
contaminated sites.
|
|
Uses
of this software include:
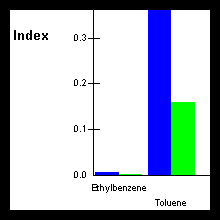
- Estimate human health risk from
exposure to contaminated media
- Estimate
risk-based clean-up levels in various media
- Perform
simple fate and transport modeling
- Evaluate potential
impacts to surface water and sediment
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
- RISC
is useful for several scenarios as part of a risk assessment:
- Calculate
clean-up levels in soil and groundwater using MCLs
(Maximum Concentration Levels) or user-defined concentrations in groundwater or surface water as
targets
- Estimate
exposure point water and air (both indoor and outdoor)
concentrations using predictive chemical fate and
transport models
- Determine
how far down gradient a groundwater plume will go before
stabilizing using a specific degradation rate
- Predict
the maximum future concentration expected at a receptor
location
- Predict
human health risk from ‘irrigation pathways’ for
groundwater used outdoors but not supplying indoor uses
- Determine
human health risk from ingestion of vegetables grown in
contaminated soil or irrigated with contaminated
groundwater
- Use
surface water mixing models to estimate potential impacts
to surface water and sediments from contaminated
groundwater
- Determine
if a more sophisticated model is needed
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
RISC Key Features:
click to enlarge
|
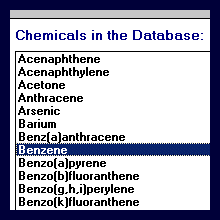
Customizable
Chemical Database:
The user may
choose chemicals of concern
from a standard library of 86 chemicals; the user may
add or delete chemicals from the library and alter the
physical, chemical and toxicological properties of
each.
The database includes the
following chemical properties: vapor
pressure, solubility, Henry's Law coefficient, log
octanol/water partition coefficient (log Kow),
organic carbon partition coefficient (Koc),
inorganic partition coefficient (Kd),
diffusive coefficients in air and water degradation
rates and vegetable uptake factor.
The database also includes the
following toxicological properties: USEPA
carcinogenic classification, toxicity parameters
(cancer potency factor and reference dose), absorption adjustment factors
and skin permeability coefficient.
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Surface
Water and Sediment Criteria Database:
RISC 4.0 has a large surface
water and sediment criteria database containing data for several different countries, allowing the
user to compare modeled surface water and sediment
criteria with regulatory standards from around the world.
- The
RISC database contains freshwater
and marine surface water criteria from
the following databases:
- United
Stated Environmental Protection Agency Ambient
Water Quality Criteria
- United
Kingdom Environmental Quality Standards
- Australia
and New Zealand Environmental and Conservation
Council Guideline for the Protection of Aquatic
Ecosystems
- European
Commission Water Quality Objective
- Canadian
Council of Ministers for the Environment
Freshwater Aquatic Life Guideline
- The sediment criteria
in the database is from the National Oceanographic
and Atmospheric Administration
|
|
click to enlarge
|
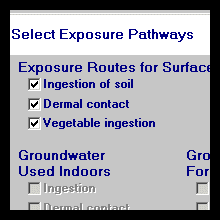
Numerous
Exposure Pathways:
RISC can be used to estimate
the potential for adverse human health impacts (both
carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic) from several
exposure pathways including:
-
Ingestion of soil
-
Dermal contact with soil
-
Ingestion
of groundwater
-
Dermal contact with groundwater
-
Dermal intake in the shower
-
Inhalation in the shower
-
Inhalation of outdoor air
-
Inhalation of indoor air
-
Ingestion of surface water
-
Dermal contact with surface water
-
Ingestion of vegetables grown in
contaminated soils
-
Ingestion of vegetables irrigated with
groundwater
-
Ingestion of irrigation water
-
Dermal intake of irrigation water
-
Inhalation of irrigation water spray
RISC gives the user the ability to
calculate additive risk due to multiple pathways,
compounds and receptors.
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Tiered
RBCA Applications:
An Excel spreadsheet based on
the Risk-Based Corrective Action (RBCA) algorithms can
be used to replicate the tiered RBCA process
- RBCA is a decision-making
process for assessment and response to subsurface
contamination and is based on protection of human
health and environmental resources.
- The RISC software has an
extensive Excel spreadsheet that can be used as a screening
tool
- The spreadsheet contains all
of the chemicals in the RISC software
- The input values in the
spreadsheet are customizable so that multiple
Risk-Based Screening Levels (RBSLs) tables can be
generated (i.e. different soil types) and saved
under different file names.
Basic Steps
in a Risk Assessment
Tier 1: Excel Spreadsheet Comparison
-
Tier
1 involves initial site assessment and
classification of the site based on conservative
RBSL that are
non-site specific.
-
The
spreadsheet can be used ‘as is’ for a Tier 1
look-up table
-
Default
values may be modified to create Tier 1 tables for
new receptors or exposure scenarios.
Tier 2: Fate and Transport Modeling
-
Tier
2 involves evaluating the site using more
site-specific information and/or evaluating
alternative compliance points
-
The
RISC software package contains fate and transport
models that may be used to develop site-specific
clean-up levels which are applicable to Tier 2
analysis
-
The
user can also perform probabilistic exposure
evaluations using RISC's Monte Carlo option
with site-specific data for a Tier 3 analysis
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Fate
and Transport Modeling:
Fate and transport models in
RISC are designed to be used to estimate receptor
point concentrations as part of a risk assessment.
- Fate
and transport models can distinguish between the
presence or absence of phase-separated product (NAPL)
in the source zone
- Analytical
models in the software include: vadose zone
leaching model, groundwater model, and a saturated
soil model (for NAPL at the watertable)
- Volatilization
models for indoor and outdoor air and simple
groundwater to surface water interactions
- The
groundwater models simulate three-dimensional
dispersion.
RISC includes the following
embedded chemical fate and transport models:
- Leaching from vadose zone
soil source to groundwater
- Saturated soil source at the
water table impacting groundwater
- Dispersion, advection,
retardation and degradation of groundwater as it
moves in an aquifer
- Emissions from soil to
outdoor and indoor air (including models
considering biodegradation)
- Emissions from groundwater to
indoor air
- Sediment partitioning and
surface water mixing models
The models listed above may
be linked together. For example, the saturated
soil model can be linked with the groundwater model
and then used to estimate volatile emissions to indoor
air at at downgradient location.
|
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Determine
Risk-Based TPH Targets:
RISC allows
the user to determine risk-based TPH (total petroleum
hydrocarbon) targets using the TPH fractions proposed
by the U.S. Air Force led TPH Working Group.
|
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Detailed
User's Manual:
The RISC software package
includes a comprehensive user’s manual with indepth example problems.
|
|
|
Developed
By:
Lynn R.
Spence, Spence Environmental Engineering, Pleasanton, California
Terry
Waldon, BP Oil International, Sunbury, UK
|
There's more
Click here
for additional information on RISC 4.0
|
|
|
GroundwaterSoftware.com is brought to you
by
Environmental
Software Online, LLC
520 Chicopee Row, Groton, MA 01450 USA
Tel: (978) 448-5818 Fax: (978) 772-0595
E-Mail: info@groundwatersoftware.com
|